General description
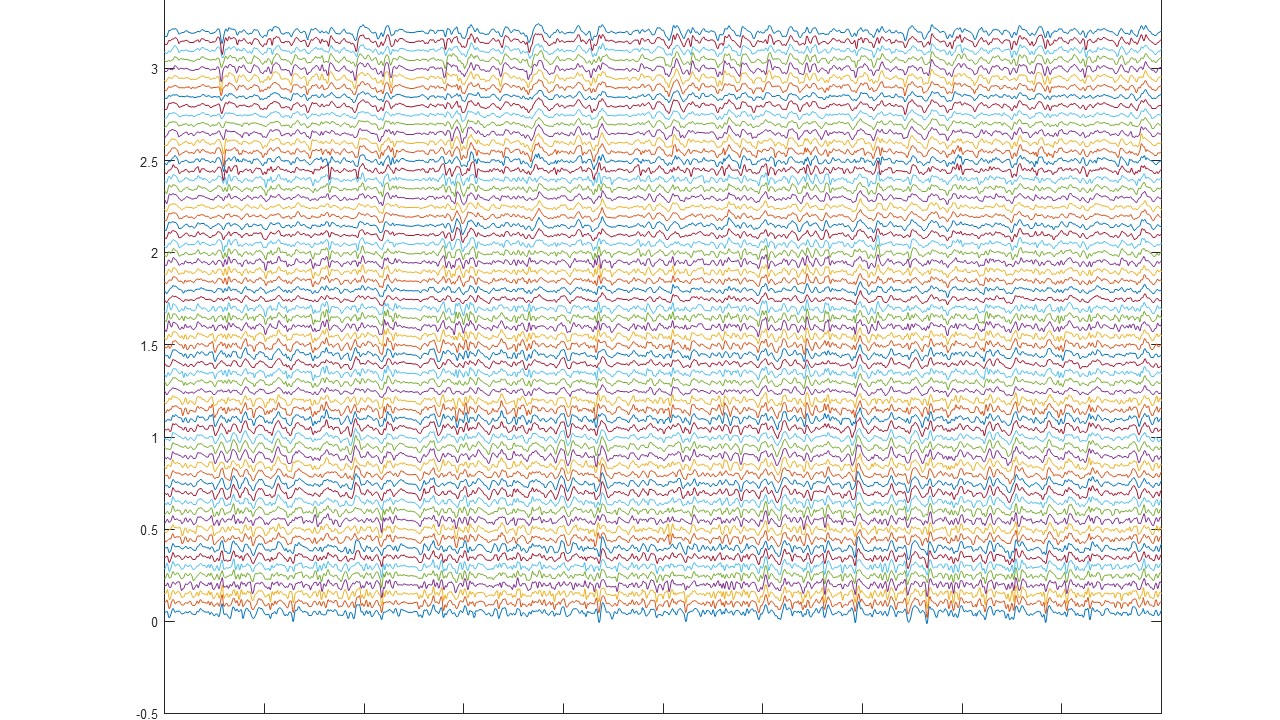
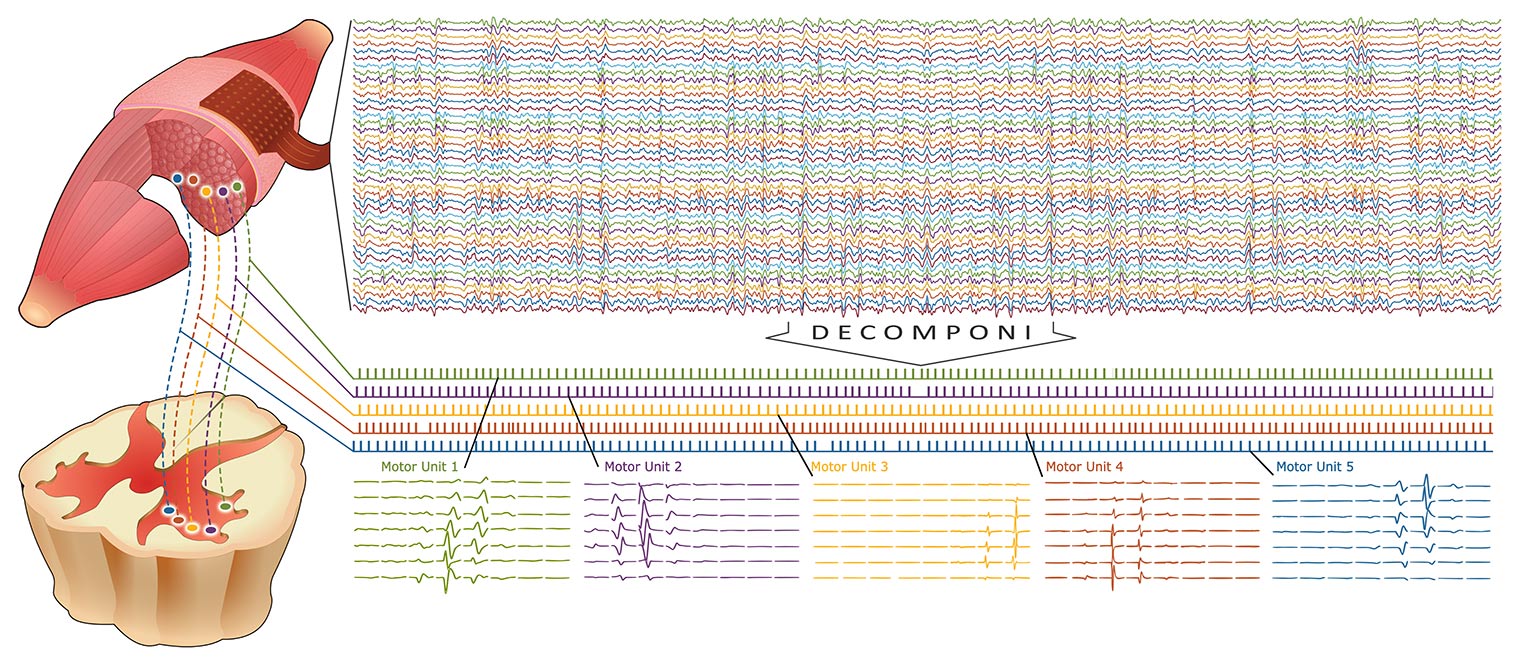
Decomponi is a tool included in the free software OT BioLab for the processing of multi-channel EMG signals recorded with non-invasive two-dimensional arrays of electrodes. It is based on blind source separation techniques and identifies the contributions of motor units to the surface EMG.
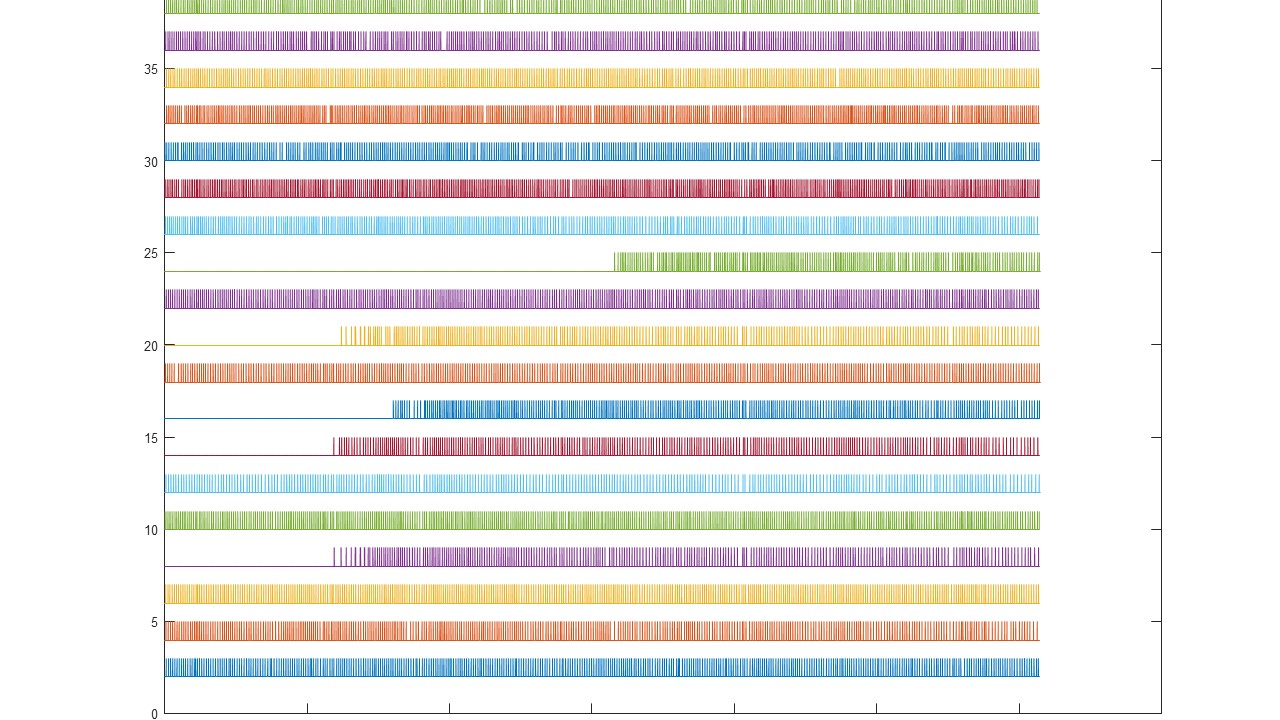
The result is a series of motor unit action potential trains that represents the neural drive sent to the muscles. In the literature, this separation approach is also called “EMG decomposition”. EMG decomposition has been classically possible only with invasive (needle) electrodes and time-consuming manual editing. Decomponi allows decomposition from fully non-invasive recordings in a fully automatic way. Decomponi has been developed by OT Bioelettronica based on research methods and results published by the groups of Prof. Dario Farina, Dr. Francesco Negro, and Prof. Ales Holobar *, who have also acted as consultants for the software implementation.
Technical specification
- Decomponi needs as input two-dimensional EMG signals recorded by arrays of >=32 electrodes per muscle
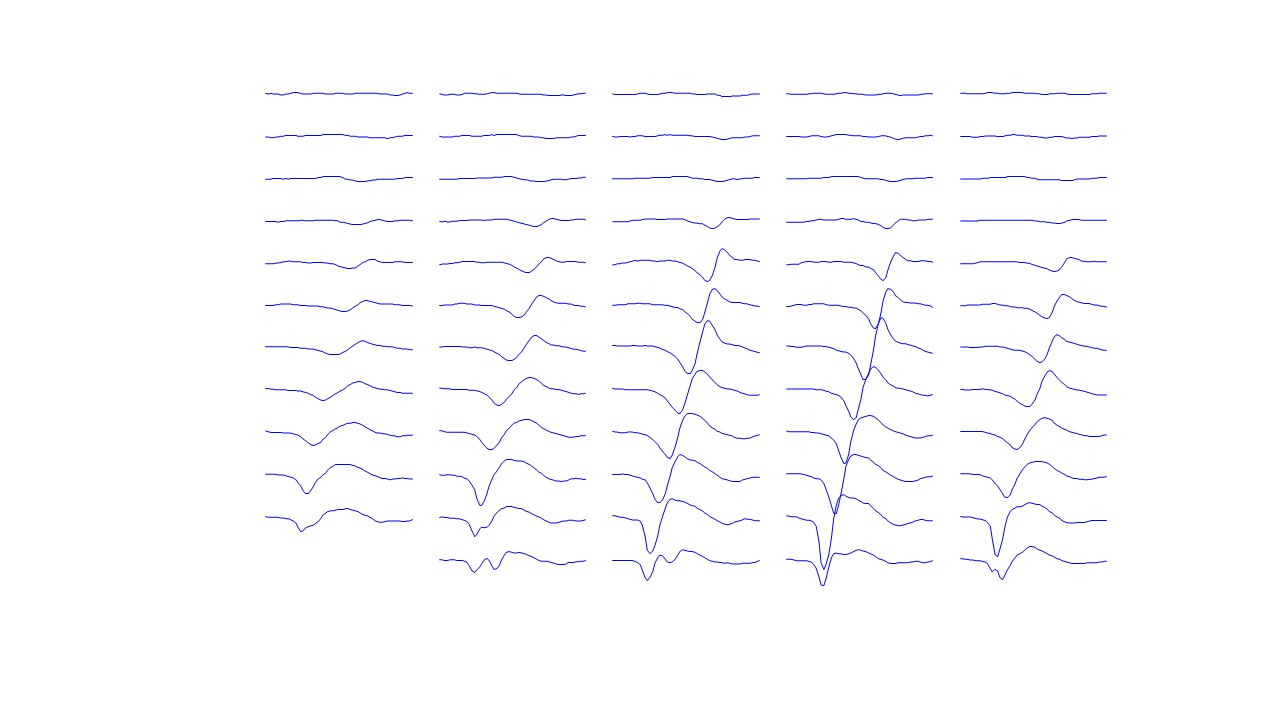
- It provides as output both the series of discharges of the identified motor units as well as the respective action potentials for each location of the recording grid
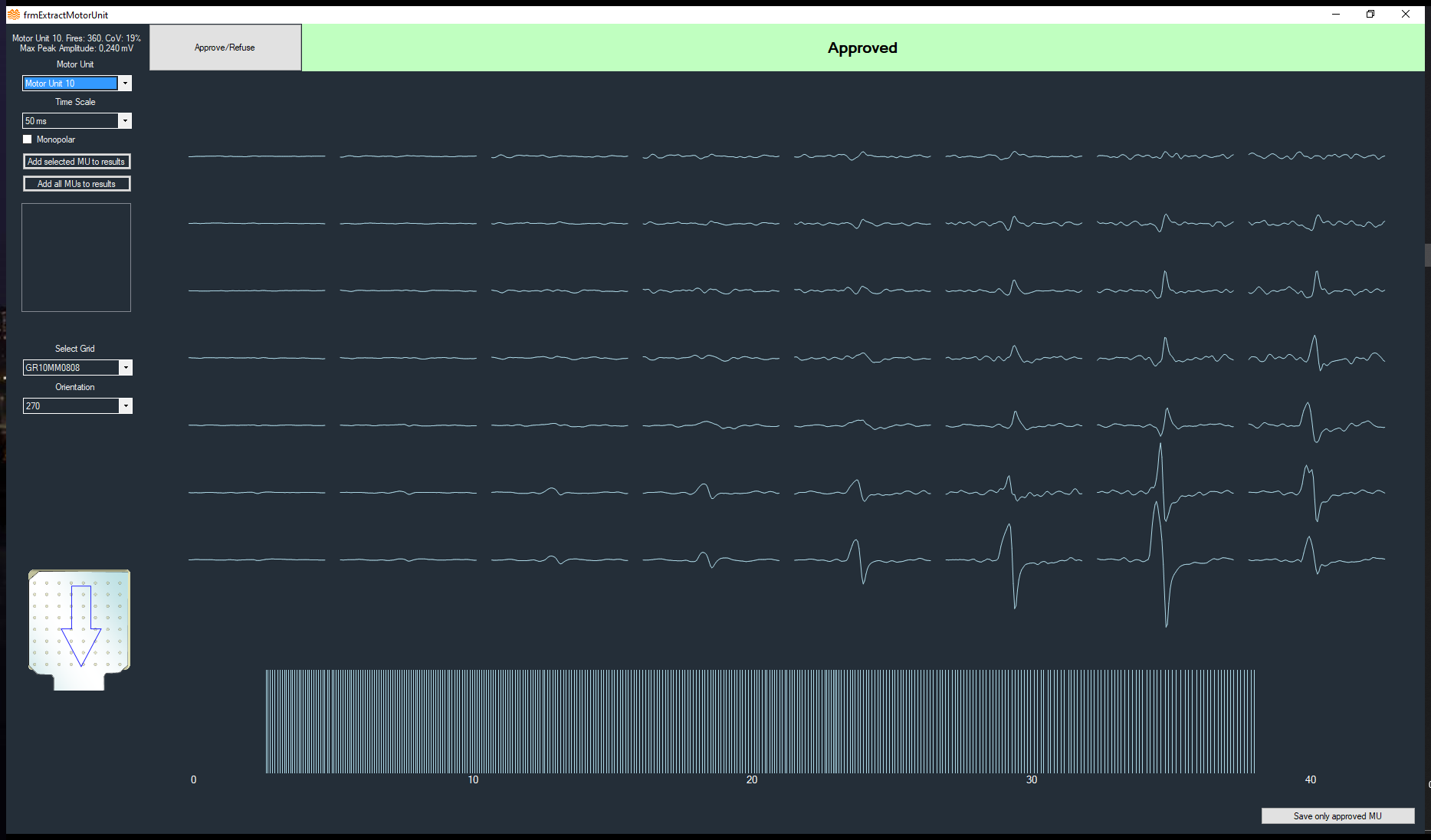
- It tests the validity of the extracted results by indexes of accuracy that have been tested in the scientific literature. Each extracted action potential train is provided with an estimated confidence of its correctness
- The number of sources estimated with high accuracy is usually approximately equal to half the number of electrodes but depends on the signal quality and, partly, on the muscle tested
- It works with signals recorded in monopolar configuration as well as in any other derivation (e.g., differential)
- It is limited to isometric contractions
- In addition to the series of discharge timings, it also provides basic statistical characteristics of the extracted motor units, such as the discharge rate and interspike interval variability
- It provides as output both the series of discharges of the identified motor units as well as the respective action potentials for each location of the recording grid
- It tests the validity of the extracted results by indexes of accuracy that have been tested in the scientific literature. Each extracted action potential train is provided with an estimated confidence of its correctness
- The number of sources estimated with high accuracy is usually approximately equal to half the number of electrodes but depends on the signal quality and, partly, on the muscle tested
- It works with signals recorded in monopolar configuration as well as in any other derivation (e.g., differential)
- It is limited to isometric contractions
- In addition to the series of discharge timings, it also provides basic statistical characteristics of the extracted motor units, such as the discharge rate and interspike interval variability